Published: May 11, 2022 by Ufkun Karaman
The purpose of this blog is to assist in setting up a high availability Kubernetes cluster.
PreRequisite
- 3 vms for Kubernetes Cluster Master Nodes (Ubuntu 20.04) for a high availability Kubernetes cluster
- 3 vms for Kubernetes Cluster Worker Nodes (Ubuntu 20.04)
- 1 vm for Kubernetes Installer Node (Ubuntu 20.04)
Architecture schema
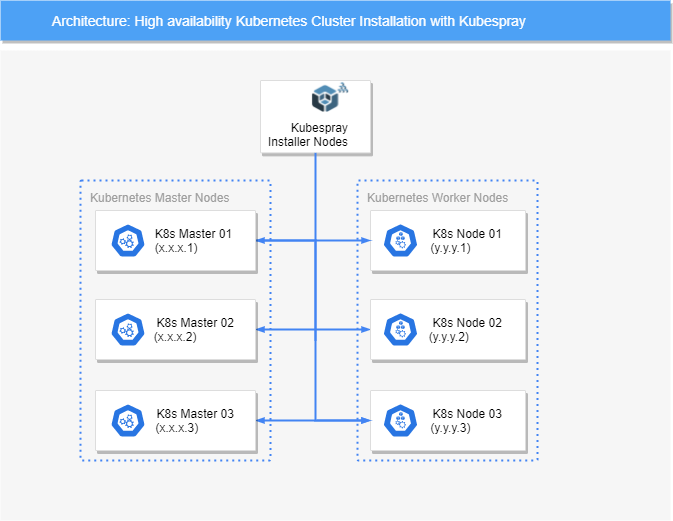
PreRequisite
K8s-Master-01(x.x.x.1)(ubuntu 20-04)
K8s-Master-02(x.x.x.2)(ubuntu 20-04)
K8s-Master-03(x.x.x.3)(ubuntu 20-04)
K8s-Worker-01(y.y.y.1)(ubuntu 20-04)
K8s-Worker-02(y.y.y.2)(ubuntu 20-04)
K8s-Worker-03(y.y.y.3)(ubuntu 20-04)
1. Kubespray Abaut
This quickstart helps to install a Kubernetes cluster hosted on GCE, Azure, OpenStack, AWS, vSphere, Packet (bare metal), Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (Experimental) or Baremetal with Kubespray.
Kubespray is a composition of Ansible playbooks, inventory, provisioning tools, and domain knowledge for generic OS/Kubernetes clusters configuration management tasks. Kubespray provides:
- a highly available cluster
- composable attributes
- support for most popular Linux distributions
- Ubuntu 16.04, 18.04, 20.04
- CentOS/RHEL/Oracle Linux 7, 8
- Debian Buster, Jessie, Stretch, Wheezy
- Fedora 31, 32
- Fedora CoreOS
- openSUSE Leap 15
- Flatcar Container Linux by Kinvolk
- continuous integration tests
2. Standard linux settings made in the operating system
-
Standard linux settings made in the operating system
3. Kubernetes HA Cluster Installing the packages required for the installation and configuring the system
Installing the packages required for the installation
-
Install HWE (MASTERS-WORKERS)
NOTE: Hardware Enablement (HWE) is an emerging technology to fix problems caused by hardware differences between new hardware and users.
apt-get -y install linux-image-generic-hwe-20.04 -y -
Installing the packages required for installing Ansible (MASTERS-WORKERS-INSTALLER NODE)
sudo apt install python3 python3-pip -y
Configuring the system for the installation
-
Disable Swap (MASTERS-WORKERS)
sudo sed -i '/ swap / s/^\(.*\)$/#\1/g' /etc/fstab sed -i 's/\/swap.img/#\/swap.img/g' /etc/fstab sudo swapoff -a -
Generate Sshkeygen (Private key) (INSALLER NODE)
ssh-keygen <user-or-root>@<hostname>:~$ ssh-keygen Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa): Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /home/username/.ssh/id_rsa Your public key has been saved in /home/username/.ssh/id_rsa.pub The key fingerprint is: .... The key's randomart image is: +---[RSA 3072]----+ | | | | | | | | | | +----[SHA256]-----+ -
Ssh Configuration (Public Key) (INSALLER NODE)
ssh-copy-id <user-or-root>@x.x.x.1 ssh-copy-id <user-or-root>@x.x.x.2 ssh-copy-id <user-or-root>@x.x.x.3 ssh-copy-id <user-or-root>@y.y.y.1 ssh-copy-id <user-or-root>@y.y.y.2 ssh-copy-id <user-or-root>@y.y.y.3 -
Download Kubespray repo and Install requirements for installation (INSALLER NODE)
mkdir /SETUP/; cd /SETUP/ wget https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray/archive/refs/tags/v2.18.1.tar.gz tar -zxvf v2.18.1.tar.gz cd kubespray-2.18.1 pip3 install -r requirements.txt -
Define Ansible Hosts files (INSALLER NODE)
cp -rfp inventory/sample inventory/mycluster declare -a IPS=(172.17.233.69 172.17.233.70 172.17.233.71 172.17.233.68 172.17.233.66) CONFIG_FILE=inventory/mycluster/hosts.yaml python3 contrib/inventory_builder/inventory.py \${IPS[@]} $ vim inventory/**mycluster/hosts.yaml** ### all: hosts: master1: ansible_host: x.x.x.1 ip: x.x.x.1 access_ip: x.x.x.1 master2: ansible_host: x.x.x.2 ip: x.x.x.2 access_ip: x.x.x.2 master3: ansible_host: x.x.x.3 ip: x.x.x.3 access_ip: x.x.x.3 node1: ansible_host: y.y.y.1 ip: y.y.y.1 access_ip: y.y.y.1 node2: ansible_host: y.y.y.2 ip: y.y.y.2 access_ip: y.y.y.2 node3: ansible_host: y.y.y.3 ip: y.y.y.3 access_ip: y.y.y.3 children: kube_control_plane: hosts: master1: master2: master3: kube-node: hosts: node1: node2: node3: etcd: hosts: master1: master2: master3: k8s-cluster: children: kube_control_plane: kube-node: calico-rr: hosts: {}
Setting Containerd (INSALLER NODE)
-
Define Cluster Name, Network Plugin, Kubernetes Version, Kube Proxy, Dns
$ vim inventory/mycluster/group_vars/k8s_cluster/k8s-cluster.yml ###... BE CARAFULL LOWERCASE. ### cluster_name: cluster-name-k8s-cluster (devops.k8s.cluster) ## Change this to use another Kubernetes version, e.g. a current beta release kube_version: v1.22.5 # Choose network plugin (cilium, calico, weave or flannel. Use cni for generic cni plugin) # Can also be set to 'cloud', which lets the cloud provider setup appropriate routing kube_network_plugin: flannel # Kube-proxy proxyMode configuration. # Can be ipvs, iptables kube_proxy_mode: ipvs # Can be coredns, coredns_dual, manual or none dns_mode: coredns -
Define Etcd confugration group_vars/etcd.yml
$ vim inventory/mycluster/group_vars/etcd.yml ## Settings for etcd deployment type etcd_deployment_type: host -
Define Registry (group_vars/all/containerd.yml)
$ vim inventory/mycluster/group_vars/all/containerd.yml ... containerd_registries: "devops.registry.io": "https://devops.registry.io"
4. Let’s Start Installation (INSALLER MASTER)
- Control Ansible Playbook (INSALLER MASTER)
ansible-inventory -i inventory/mycluster/hosts.yaml --list
- Installation (INSALLER MASTER)
#user
ansible-playbook -i inventory/mycluster/hosts.yaml --become --become-user=root cluster.yml --extra-vars "ansible_sudo_pass=password"
### OR ###
#username root
ansible-playbook -i inventory/mycluster/hosts.yaml cluster.yml -u root
5. Control K8s Cluster (MASTER)
- Ports and Protocols
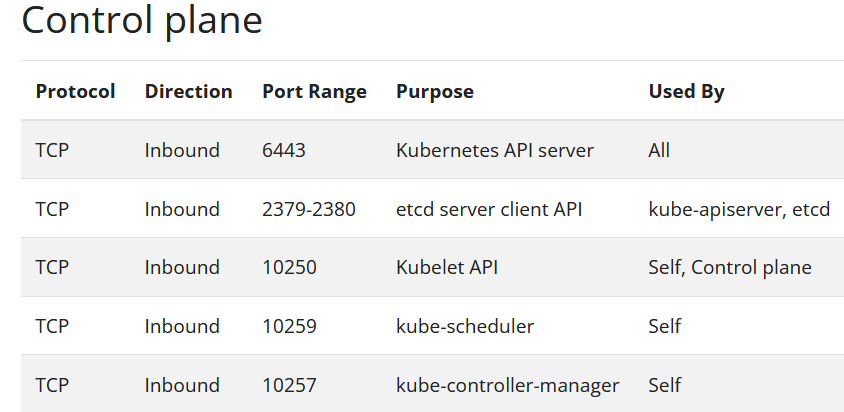
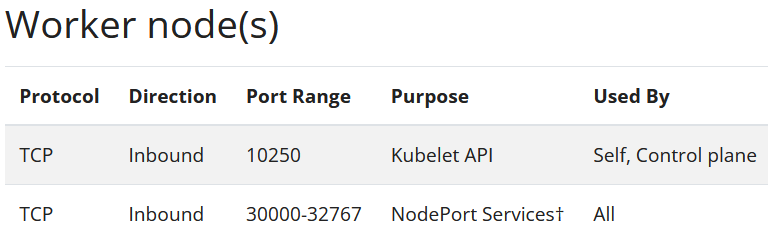
-
Control (MASTER)
kubectl version --client # Kubernetes cli version kubectl config view --minify -o jsonpath='{.clusters[].name}' # Kubernetes cluster name control kubectl get cs # Kubernetes components control kubectl get nodes # Kubernetes nodes control


