Published: Jul 18, 2022 by Ufkun Karaman
Keda
KEDA is a Kubernetes-based Event Driven Autoscaler. With KEDA, you can drive the scaling of any container in Kubernetes based on the number of events needing to be processed.
KEDA is a single-purpose and lightweight component that can be added into any Kubernetes cluster. KEDA works alongside standard Kubernetes components like the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler and can extend functionality without overwriting or duplication. With KEDA you can explicitly map the apps you want to use event-driven scale, with other apps continuing to function. This makes KEDA a flexible and safe option to run alongside any number of any other Kubernetes applications or frameworks.
How KEDA works
KEDA performs two key roles within Kubernetes:
-
Agent — KEDA activates and deactivates Kubernetes Deployments to scale to and from zero on no events. This is one of the primary roles of the keda-operator container that runs when you install KEDA.
-
Metrics — KEDA acts as a Kubernetes metrics server that exposes rich event data like queue length or stream lag to the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler to drive scale out. It is up to the Deployment to consume the events directly from the source. This preserves rich event integration and enables gestures like completing or abandoning queue messages to work out of the box. The metric serving is the primary role of the keda-operator-metrics-apiserver container that runs when you install KEDA.
Architecture
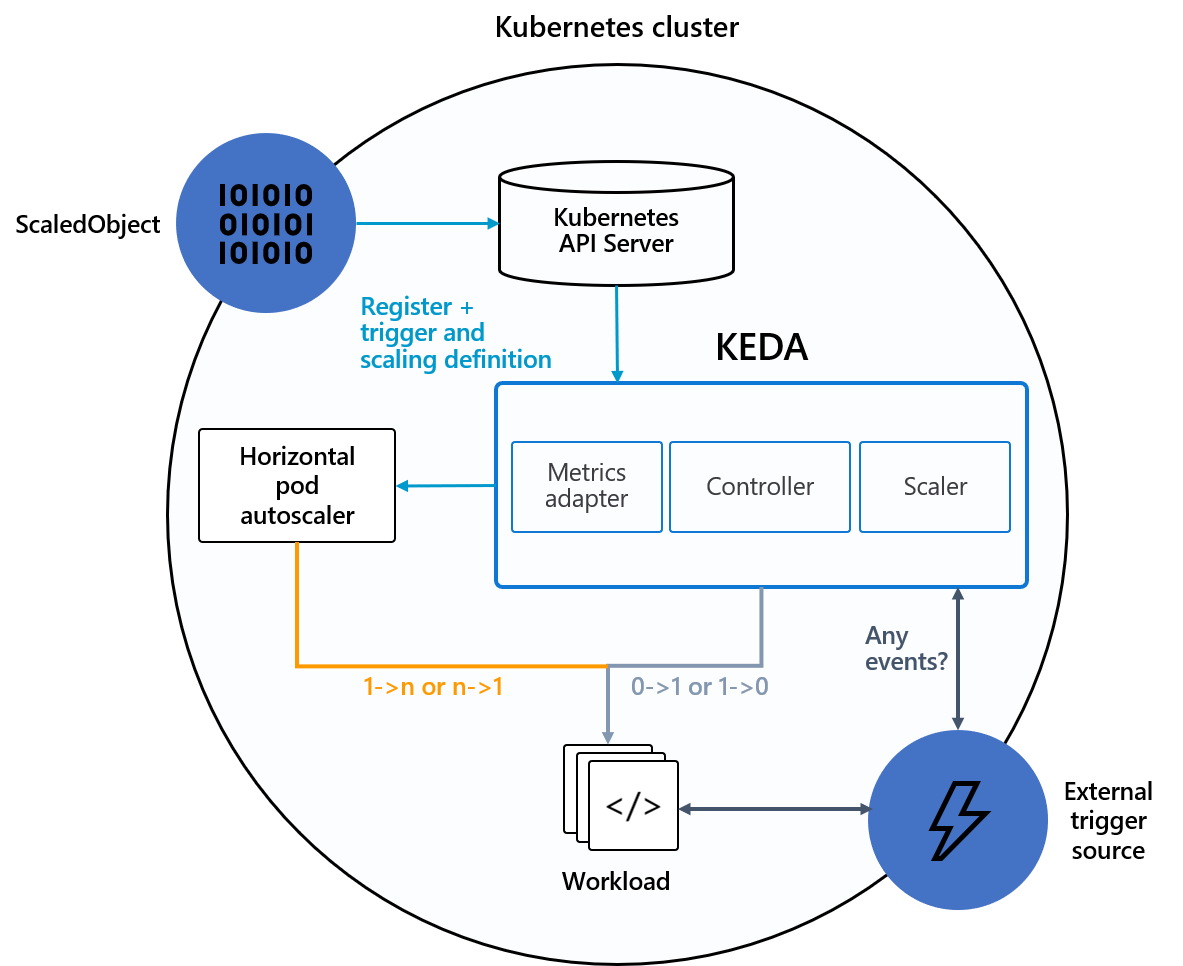
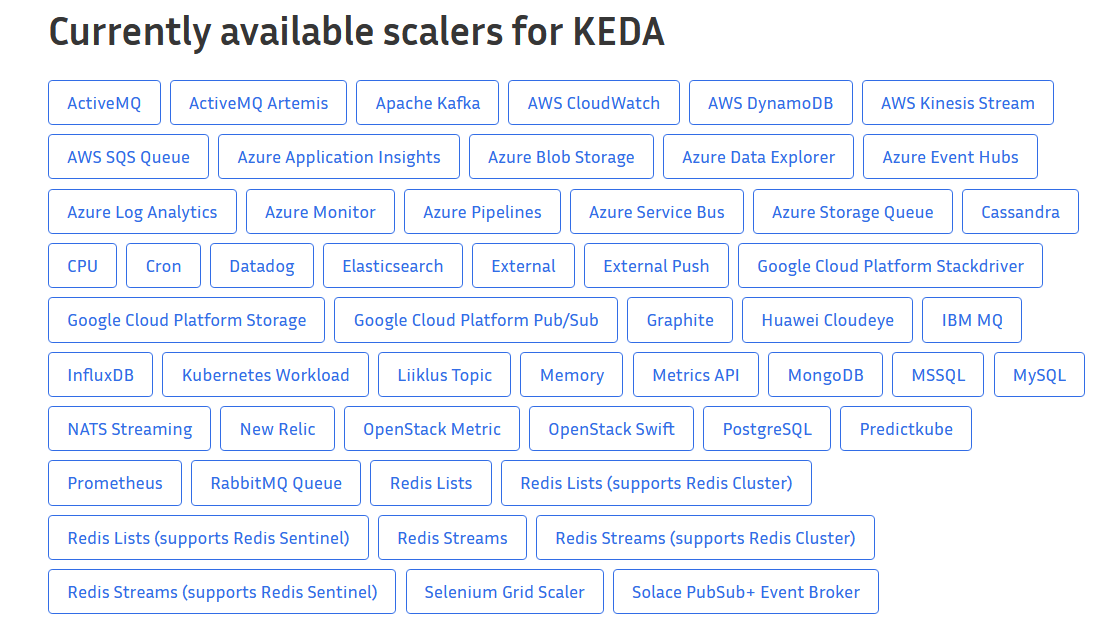 For the current scaler list: keda.sh
For the current scaler list: keda.sh
Keda Installation
Deploying KEDA with Helm is very simple:
-
Add Helm repo
helm repo add kedacore https://kedacore.github.io/charts helm repo update -
Define namespace and Install keda Helm chart
#define namespace kubectl create namespace kedadf #Install keda Helm chart helm install keda kedacore/keda --namespace keda - Check Deployment
-
You can view the KEDA operator pod via kubectl:
$ kubectl get pods -n keda NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE keda-operator-7879dcd589-fb9x8 1/1 Running 0 17d keda-operator-metrics-apiserver-54746f8fdc-bsrlh 1/1 Running 0 17d -
You can view the logs for the keda operator container with the following:
kubectl logs -n keda keda-operator-7879dcd589-fb9x8 -c keda-operator -
You can view apiserver logs for
kubectl get apiservice v1beta1.external.metrics.k8s.io
-
- Sample Keda Yaml
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1
kind: ScaledObject
metadata:
name: v2-ingress-requests
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
kind: Deployment # Optional. Default: Deployment
name: hello-world # Mandatory. Must be in the same namespace as the ScaledObject
pollingInterval: 15 # Optional. Default: 30 seconds
cooldownPeriod: 30 # Optional. Default: 300 seconds
minReplicaCount: 1 # Optional. Default: 0
maxReplicaCount: 5 # Optional. Default: 100
triggers:
- type: prometheus
metadata:
serverAddress: http://prometheus-server.prometheus.svc.cluster.local
metricName: nginx_ingress_controller_requests
threshold: '5'
query: sum(rate(nginx_ingress_controller_requests{path="/v2"}[2m]))


